Every radio in ACRE can be equipped with at least one antenna. Since radios usually have specific antennas designed and tuned for the radio and the frequency range used, it is likely one must add a new antenna if a new radio is created for ACRE.
In order to allow an antenna to work properly in ACRE, there are a few required config entries and most importantly a set of gain data covering the desired frequency range. The gain data is used by the signal processing functions for calculation of signal strengths. For basics refer to Radio Loss.
Example Antenna Config
Antennas themselves are defined in the sys_antennas component of ACRE2 sys_antennas/CfgAcreComponents.hpp. The parameters should be self explanatory as the following examples shows.
class CfgAcreComponents {
class ACRE_ComponentBase;
class ACRE_BaseAntenna: ACRE_ComponentBase {
type = ACRE_COMPONENT_ANTENNA;
simple = true;
polarization = VERTICAL_POLARIZE;
heightAG = AVERAGE_MAN_HEIGHT;
orient = 90; // in degrees off of flat plane
name = "Default Antenna";
connector = ACRE_CONNECTOR_TNC;
height = 1.2; //meters
binaryGainFile = QPATHTOF(binary\VHF_1.2m_whip_gain.aba);
};
class ACRE_2HALFINCH_UHF_TNC: ACRE_BaseAntenna {
name = "2.5 Inch UHF Antenna AN/PRC-343 ONLY";
connector = ACRE_CONNECTOR_TNC;
height = 0.062457; //meters
binaryGainFile = QPATHTOF(binary\prc343_gain.aba);
};
};
Generating Antenna Gain Data
As ACRE tries to simulate radios as close to reality as possible, the gain data used is coming from a tool used for antenna and electromagnetic effects simulation. This tool is called 4NEC2 and can be obtained for free: 4NEC2. For installation instructions and a bunch of good tutorials, please refer to the website.
Setting up the antenna
The first step after opening 4NEC2 is to create a model of the antenna. Usually it is more than sufficient to use a vertical wire and a simple ground setting. These models are stored in the .nec format which is basically a text file. The .nec files from all existing antennas could be found in the extras/antenna folder and a good practice is to simply take an existing file and change the parameters either in a text editor or directly in 4NEC2.
Ground Settings: It is highly recommended to set the ground setting to Perfect gnd and check the Connect wire(s) for Z=0 to ground setting as well. Other ground settings may lead to more realistic results regardings the antenna gain field but in contrary to the real world, ACRE2 does not simulate ground effects like ground propagation. The end result in-game would be unexplainable transmission-losses even in perfect conditions.
Calculating antenna gain
Calculation of antenna gain can be done directly in 4NEC2 by pressing F7. To ensure the result to be usable by ACRE2, the setup shown in the figure below is highly recommended.
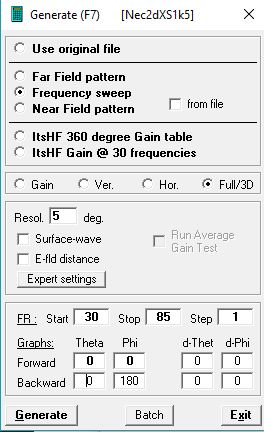
A resolution of 5 Degrees is a good trade-off between file size/calculation speed and later in-game precision. Before calculating the frequency range must be set correctly. The actual values depend on the frequency range of the antenna/radio and a step size of 1(MHz) is recommended. While the lower limit can be on the minimal frequency, the higher limit must be 1-2 MHz over the highest used frequency. To perform the calculation, press the button TBC. Note: As 4NEC2 is only capable of 256 frequency steps, the step size must be set to a higher value of the frequency range is higher than 256.
The resulting files
4NEC2 creates two files after finishing the calculation process. One with the ending *.inp and the other one with *.out. The input file *.inp looks very similar to the *.nec file, with the difference that it contains the specific input data for the calculation (the parameters, we entered in the calculation window earlier). The output file *.out contains all the generated gain data plus a bunch of additional data.
Note: 4NEC2 sometimes doesn’t name the two files correctly. The input file’s name seems to be cut off after a few characters. As the file names need to be the same for the python script to work properly, rename them.
Writing binary files to ACRE2
The first step is to copy both *.inp and *.out files to the correct location in your ACRE2 development folder. E.g. <ACRE2 development directory>\extras\antennas. After that simply start a Command Prompt (Win) or Terminal (Linux) instance and navigate to the tools folder. The python script we are looking for is antenna_create_binary.py. Start it with a single parameter: The name of the input/output files. If we stay at the PRC343 antenna as an example, the command should be like this: python antenna_create_binary.py prc343. After waiting for a few seconds, the script will tell you how many bytes were written to which file.
Create Antenna config entry
The final step is to create a config entry for the antenna like shown at the beginning of this page. Of course you need to bind the antenna to the radio as described in new radio. A detailed testing should always be mandatory to ensure there is no error in the generated gain file.